POLLUTION AND ENVIRONMENT DEGRADATION
Table of contents
1. Geneology
2. Gist
3. Summary
4. Detailed View
5.Detailed View in Tamil ( தமிழில் விரிவான உள்ளடக்கம் )
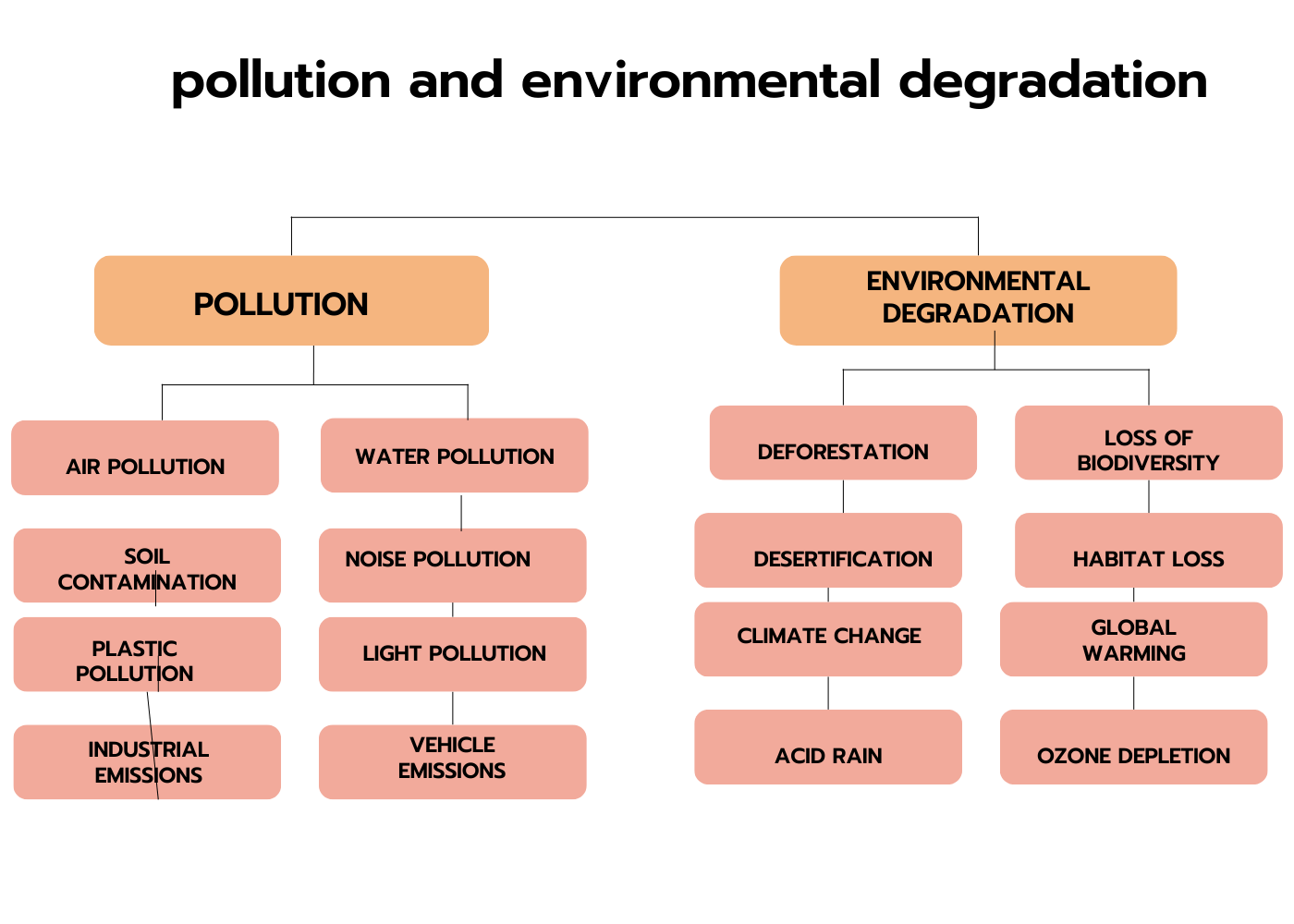
Geneology
Gist
Types of Pollution
• Air pollution: Contamination of the atmosphere with harmful
gases, particles, and aerosols from sources like transportation,
industrial activities, and burning fossil fuels.
• Water pollution: Introduction of pollutants like chemicals,
bacteria, and other harmful substances into water bodies, impacting
aquatic life and water quality.
• Soil pollution: Contamination of soil with chemicals, heavy
metals, pesticides, and other harmful substances, impacting plant growth
and soil fertility.
• Noise pollution: Excessive and unwanted sounds from various
sources, causing health problems like hearing loss, stress, and sleep
disturbance.
• Light pollution: Excessive artificial light at night that
disrupts natural light cycles and impacts wildlife behavior.
Environmental Degradation
• Deforestation: Loss of tree cover due to human activities like
logging, agriculture, and infrastructure development, leading to soil
erosion, biodiversity loss, and disruption of water cycles.
• Land degradation: Loss of the ability of land to support life
due to factors like overgrazing, deforestation, and improper irrigation
practices.
• Climate change: Long-term alteration of temperature and
weather patterns primarily due to human-induced greenhouse gas
emissions, impacting natural ecosystems, sea levels, and weather
patterns.
Impacts of Pollution and Environmental Degradation
• Loss of biodiversity: These issues contribute to the extinction
and endangerment of various plant and animal species, disrupting
ecological balance.
• Human health problems: Exposure to pollutants can lead to
respiratory problems, heart disease, cancer, and other health issues.
• Disruption of natural resources: Air, water, and soil pollution
affect the quality and availability of these essential resources.
• Economic consequences: Environmental degradation can lead to
increased healthcare costs, reduced agricultural productivity, and
damage to infrastructure
Solutions and Mitigating Actions
• Transitioning to renewable energy sources: Reducing dependence
on fossil fuels and increasing reliance on cleaner energy
alternatives.
• Sustainable resource management: Implementing practices like
responsible waste management, improved land management, and water
conservation.
• Promoting clean technologies: Developing and adopting cleaner
technologies for industrial processes and transportation.
• Policy and regulatory changes: Implementing stricter
environmental regulations and enforcing existing ones effectively.
• Raising awareness and public participation: Educating the
public about the importance of environmental protection and encouraging
individual actions towards a sustainable future.
• Overall, tackling pollution and environmental degradation requires a
comprehensive and collaborative approach involving individuals,
governments, and international organizations. By implementing
sustainable practices and upholding environmental responsibility, we can
strive for a cleaner, healthier planet for ourselves and future
generations.
Summary
• Pollution and environmental degradation are critical global challenges
with far-reaching impacts on ecosystems, human health, and socioeconomic
well-being. Various types of pollution, including air, water, soil,
noise, and light pollution, arise from industrial activities,
transportation, agriculture, waste management, and urbanization. These
pollutants, such as chemicals, particulate matter, and greenhouse gases,
degrade ecosystems, harm wildlife, and pose risks to human health.
• The causes of pollution are multifaceted, stemming from human
activities such as industrial production, transportation, agriculture,
and urban development. These activities release pollutants into the
environment, leading to air and water contamination, soil degradation,
and habitat destruction. Pollution has significant impacts on human
health, ecosystems, and climate stability, exacerbating existing
environmental pressures and contributing to socioeconomic inequalities.
Detailed Content
Types of Pollution
1.Air Pollution
Air pollution occurs when harmful substances, such as particulate
matter, gases, and chemicals, are released into the atmosphere. Sources
of air pollution include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust,
agricultural activities, and natural processes like volcanic eruptions.
Common air pollutants include nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide
(SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O3), and volatile organic compounds
(VOCs).
2.Water Pollution
Water pollution occurs when contaminants are discharged into bodies of
water, such as rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater. Sources of water
pollution include industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, sewage and
wastewater, oil spills, and improper waste disposal. Pollutants can
include heavy metals, pesticides, fertilizers, pathogens, and
plastics
3.Soil Pollution
Soil pollution, also known as land pollution, involves the contamination
of soil by hazardous substances. This can result from industrial
activities, mining operations, improper waste disposal, and the use of
agrochemicals such as pesticides and herbicides. Soil pollution can
degrade soil fertility, harm plant and animal life, and pose risks to
human health through the consumption of contaminated food and water.
4.Noise Pollution
Noise pollution refers to excessive or disruptive noise levels that can
have adverse effects on human health and wildlife. Sources of noise
pollution include transportation (e.g., traffic, aircraft), industrial
activities, construction sites, and recreational activities. Prolonged
exposure to high noise levels can lead to hearing loss, stress, sleep
disturbances, and other health problems in humans, while disrupting
communication and behavior patterns in animals.
5.Light Pollution
Light pollution occurs when artificial light sources, such as
streetlights, outdoor lighting, and urban development, produce excessive
or misdirected light that interferes with natural night environments.
Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems, affecting wildlife behavior,
migration patterns, and reproductive cycles. It also contributes to
wasted energy and obscures views of the night sky, impacting
astronomical research and human cultural experiences.
Causes of Pollution
1.Industrial Activities
Industrial processes, including manufacturing, power generation, and
mining, release large quantities of pollutants into the air, water, and
soil. Emissions from factories, power plants, and refineries contain
pollutants such as particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides,
heavy metals, and volatile organic compounds.
2.Transportation
The combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles, airplanes, ships, and other
transportation modes is a major source of air pollution, releasing
pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and
particulate matter. In addition to air pollution, transportation
activities can also contribute to noise pollution, habitat
fragmentation, and wildlife mortality through collisions.
3.Agriculture
Agricultural practices, including the use of chemical fertilizers,
pesticides, and herbicides, contribute to water and soil pollution.
Runoff from agricultural fields can carry excess nutrients, pesticides,
and sediment into nearby water bodies, leading to eutrophication,
contamination of drinking water sources, and loss of biodiversity.
4.Waste Management
Improper waste disposal, including landfilling, open burning, and
illegal dumping, results in the release of pollutants into the
environment. Landfills produce methane gas, a potent greenhouse gas,
while burning waste generates air pollutants and toxic ash. Plastic
waste, in particular, poses significant challenges due to its
persistence in the environment and harmful effects on marine life.
5.Urbanization and Development
Urbanization and urban sprawl contribute to various forms of pollution,
including air pollution from vehicle emissions and industrial
activities, water pollution from runoff and sewage, soil pollution from
construction activities and waste disposal, and light pollution from
artificial lighting. Deforestation and habitat destruction associated
with development also exacerbate environmental degradation and
biodiversity loss.
Impacts of Pollution and Environmental Degradation
1.Human Health
Pollution poses significant risks to human health, causing respiratory
diseases, cardiovascular problems, neurological disorders, and various
cancers. Air pollution, in particular, is a leading cause of premature
death worldwide, contributing to millions of deaths annually. Waterborne
diseases, such as cholera and dysentery, are also prevalent in areas
with contaminated water sources.
2.Ecosystems
Pollution and environmental degradation can have profound impacts on
ecosystems, disrupting food webs, altering habitats, and reducing
biodiversity. Contaminants in water bodies can harm aquatic organisms,
including fish, amphibians, and invertebrates, while air pollution can
damage vegetation and soil quality. Habitat destruction and
fragmentation further threaten species survival and ecosystem
resilience.
3.Climate Change
Pollution, especially greenhouse gas emissions from human activities,
contributes to climate change by trapping heat in the Earth's
atmosphere. This leads to global warming, rising sea levels, more
frequent and severe weather events, altered precipitation patterns, and
shifts in ecosystems and species distributions. Climate change
exacerbates existing environmental pressures and poses additional
challenges to human societies and ecosystems
4.Socioeconomic Impacts
Pollution and environmental degradation disproportionately affect
vulnerable populations, including low-income communities, indigenous
peoples, and marginalized groups. These communities often bear the brunt
of pollution-related health problems, environmental injustices, and loss
of livelihoods. Environmental degradation can also undermine economic
development, reducing ecosystem services, agricultural productivity, and
tourism revenues.
Solutions to Pollution and Environmental Degradation
1.Policy and Regulation
Effective environmental governance, including laws, regulations, and
enforcement mechanisms, is essential for addressing pollution and
environmental degradation. Governments at the local, national, and
international levels play a critical role in setting standards,
monitoring pollution levels, and implementing measures to mitigate
environmental impacts. Policies such as emissions trading schemes,
pollution taxes, and environmental impact assessments can incentivize
pollution reduction and sustainable development.
2.Technological Innovation
Advancements in technology, such as cleaner production processes,
renewable energy technologies, and pollution control technologies, offer
opportunities to reduce pollution and promote environmental
sustainability. Investments in research and development can lead to the
development of more efficient and environmentally friendly technologies
across various sectors, including energy, transportation, agriculture,
and waste management.
3.Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable practices and promoting eco-friendly lifestyles can
help minimize pollution and environmental degradation. This includes
reducing resource consumption, minimizing waste generation, conserving
energy, promoting recycling and reuse, and supporting sustainable
agriculture and land use practices. Individuals, businesses, and
communities all have a role to play in transitioning to more sustainable
and environmentally responsible behaviors.
4.Education and Awareness
Raising public awareness and promoting environmental education are key
strategies for addressing pollution and environmental degradation.
Education campaigns can inform individuals about the causes and
consequences of pollution, empower them to take action, and foster a
sense of environmental stewardship and responsibility. Environmental
education programs in schools, community outreach initiatives, and media
campaigns can all contribute to building a more environmentally
conscious society.
5.International Cooperation
Given the transboundary nature of pollution and environmental issues,
international cooperation is essential for addressing these challenges
effectively. Multilateral agreements, such as the Paris Agreement on
climate change and the Stockholm Convention on persistent organic
pollutants, provide frameworks
தமிழில் விரிவான உள்ளடக்கம்
மாசு வகைகள்
1.காற்று மாசுபாடு
துகள்கள் போன்ற தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் பொருட்கள் போது காற்று மாசுபாடு
ஏற்படுகிறது பொருள், வாயுக்கள் மற்றும் இரசாயனங்கள் வளிமண்டலத்தில்
வெளியிடப்படுகின்றன. ஆதாரங்கள் காற்று மாசுபாடு தொழில்துறை உமிழ்வுகள்,
வாகன வெளியேற்றம், விவசாய நடவடிக்கைகள், மற்றும் எரிமலை வெடிப்புகள் போன்ற
இயற்கை செயல்முறைகள். நைட்ரஜன் ஆக்சைடுகள் (NOx), சல்பர் டை ஆக்சைடு ஆகியவை
பொதுவான காற்று மாசுபாடுகளாகும் (SO2), கார்பன் மோனாக்சைடு (CO), ஓசோன்
(O3) மற்றும் ஆவியாகும் கரிம சேர்மங்கள் (VOCகள்).
2.நீர் மாசுபாடு
அசுத்தங்கள் உடல்களில் வெளியேற்றப்படும் போது நீர் மாசுபாடு ஏற்படுகிறது
ஆறுகள், ஏரிகள், பெருங்கடல்கள் மற்றும் நிலத்தடி நீர் போன்ற நீர். நீர்
ஆதாரங்கள் தொழில்துறை வெளியேற்றங்கள், விவசாய கழிவுகள், கழிவுநீர் மற்றும்
மாசுபாடு ஆகியவை அடங்கும் கழிவு நீர், எண்ணெய் கசிவுகள் மற்றும் முறையற்ற
கழிவுகளை அகற்றுதல். மாசுபடுத்திகள் முடியும் கன உலோகங்கள்,
பூச்சிக்கொல்லிகள், உரங்கள், நோய்க்கிருமிகள் மற்றும் பிளாஸ்டிக்
3.மண் மாசுபாடு
நில மாசுபாடு என்றும் அழைக்கப்படும் மண் மாசுபாடு, மாசுபாட்டை உள்ளடக்கியது
அபாயகரமான பொருட்களால் மண். இது தொழில்துறையால் ஏற்படலாம் செயல்பாடுகள்,
சுரங்க நடவடிக்கைகள், முறையற்ற கழிவுகளை அகற்றுதல் மற்றும் பயன்படுத்துதல்
பூச்சிக்கொல்லிகள் மற்றும் களைக்கொல்லிகள் போன்ற வேளாண் இரசாயனங்கள். மண்
மாசு ஏற்படலாம் மண் வளத்தை சீர்குலைத்து, தாவரங்கள் மற்றும் விலங்குகளின்
உயிர்களுக்கு தீங்கு விளைவிக்கிறது, மேலும் ஆபத்துகளை ஏற்படுத்துகிறது
அசுத்தமான உணவு மற்றும் தண்ணீரை உட்கொள்வதன் மூலம் மனித ஆரோக்கியம்.
4.ஒலி மாசுபாடு
ஒலி மாசுபாடு என்பது அதிகப்படியான அல்லது இடையூறு விளைவிக்கும் ஒலி அளவைக்
குறிக்கிறது மனித ஆரோக்கியம் மற்றும் வனவிலங்குகளில் பாதகமான விளைவுகளை
ஏற்படுத்துகின்றன. சத்தத்தின் ஆதாரங்கள் மாசுபாடு போக்குவரத்து (எ.கா.,
போக்குவரத்து, விமானம்), தொழில்துறை ஆகியவை அடங்கும் நடவடிக்கைகள்,
கட்டுமான தளங்கள் மற்றும் பொழுதுபோக்கு நடவடிக்கைகள். நீடித்தது அதிக
இரைச்சல் அளவை வெளிப்படுத்துவது காது கேளாமை, மன அழுத்தம், தூக்கம்
ஆகியவற்றுக்கு வழிவகுக்கும் இடையூறுகள் மற்றும் மனிதர்களுக்கு ஏற்படும் பிற
உடல்நலப் பிரச்சினைகள், இடையூறு விளைவிக்கும் போது விலங்குகளின் தொடர்பு
மற்றும் நடத்தை முறைகள்.
5.ஒளி மாசுபாடு
செயற்கை ஒளி மூலங்கள் போன்ற போது ஒளி மாசு ஏற்படுகிறது தெருவிளக்குகள்,
வெளிப்புற விளக்குகள் மற்றும் நகர்ப்புற வளர்ச்சி ஆகியவை அதிகமாக உற்பத்தி
செய்கின்றன அல்லது இயற்கையான இரவு சூழல்களில் குறுக்கிடும் தவறான ஒளி. ஒளி
மாசுபாடு சுற்றுச்சூழல் அமைப்புகளை சீர்குலைத்து, வனவிலங்கு நடத்தையை
பாதிக்கலாம், இடம்பெயர்வு முறைகள் மற்றும் இனப்பெருக்க சுழற்சிகள்.
அதற்கும் பங்களிக்கிறது சக்தியை வீணடித்து இரவு வானத்தின் காட்சிகளை
மறைத்து, தாக்கத்தை ஏற்படுத்துகிறது வானியல் ஆராய்ச்சி மற்றும் மனித
கலாச்சார அனுபவங்கள்.
மாசுபாட்டிற்கான காரணங்கள்
1.தொழில்துறை நடவடிக்கைகள்
உற்பத்தி, மின் உற்பத்தி, மற்றும் உட்பட தொழில்துறை செயல்முறைகள் சுரங்கம்,
காற்று, நீர், மற்றும் அதிக அளவு மாசுகளை வெளியிடுகிறது மண்.
தொழிற்சாலைகள், மின் உற்பத்தி நிலையங்கள் மற்றும் சுத்திகரிப்பு
நிலையங்களில் இருந்து வெளியேற்றப்படும் வாயுக்கள் உள்ளன துகள்கள், சல்பர்
டை ஆக்சைடு, நைட்ரஜன் ஆக்சைடுகள் போன்ற மாசுபடுத்திகள், கன உலோகங்கள்,
மற்றும் ஆவியாகும் கரிம சேர்மங்கள்.
2.போக்குவரத்து
வாகனங்கள், விமானங்கள், கப்பல்கள் மற்றும் பிறவற்றில் புதைபடிவ
எரிபொருட்களின் எரிப்பு போக்குவரத்து முறைகள் காற்று மாசுபாட்டின் முக்கிய
ஆதாரமாக உள்ளது, வெளியிடுகிறது கார்பன் மோனாக்சைடு, நைட்ரஜன் ஆக்சைடுகள்,
ஹைட்ரோகார்பன்கள் மற்றும் குறிப்பிட்ட காாியம். காற்று மாசுபாடு தவிர,
போக்குவரத்து செயல்பாடுகள் ஒலி மாசுபாடு, வாழ்விடத்திற்கும் பங்களிக்கலாம்
துண்டாடுதல், மற்றும் மோதல்கள் மூலம் வனவிலங்கு இறப்பு.
3.விவசாயம்
ரசாயன உரங்களின் பயன்பாடு உட்பட விவசாய நடைமுறைகள், பூச்சிக்கொல்லிகள்
மற்றும் களைக்கொல்லிகள், நீர் மற்றும் மண் மாசுபாட்டிற்கு பங்களிக்கின்றன.
விவசாய வயல்களில் இருந்து வெளியேறும் நீர் அதிகப்படியான ஊட்டச்சத்துக்கள்,
பூச்சிக்கொல்லிகள், மற்றும் அருகிலுள்ள நீர்நிலைகளில் வண்டல்,
யூட்ரோஃபிகேஷனுக்கு வழிவகுக்கிறது, குடிநீர் ஆதாரங்கள் மாசுபடுதல் மற்றும்
பல்லுயிர் இழப்பு.
4.கழிவு மேலாண்மை
முறையற்ற கழிவுகளை அகற்றுதல், நிலம் நிரப்புதல், திறந்த எரித்தல் மற்றும்
சட்டவிரோதமாக கொட்டுவது, மாசுகளை வெளியிடுவதில் விளைகிறது சூழல்.
நிலப்பரப்புகள் மீத்தேன் வாயுவை உருவாக்குகின்றன, இது ஒரு சக்திவாய்ந்த
பசுமை இல்ல வாயு, கழிவுகளை எரிக்கும்போது காற்று மாசுபாடுகள் மற்றும் நச்சு
சாம்பல் உருவாகிறது. நெகிழி கழிவுகள், குறிப்பாக, அதன் காரணமாக
குறிப்பிடத்தக்க சவால்களை முன்வைக்கின்றன சுற்றுச்சூழலில் நிலைத்திருப்பது
மற்றும் கடல்வாழ் உயிரினங்களுக்கு தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் விளைவுகள்.
5.நகரமயமாக்கல் மற்றும் மேம்பாடு
நகரமயமாக்கல் மற்றும் நகர்ப்புற விரிவாக்கம் பல்வேறு வகையான மாசுபாட்டிற்கு
பங்களிக்கின்றன, வாகன உமிழ்வு மற்றும் தொழில்துறையிலிருந்து காற்று
மாசுபாடு உட்பட நடவடிக்கைகள், கழிவுநீர் மற்றும் கழிவுநீரில் இருந்து நீர்
மாசுபாடு, மண் மாசுபாடு கட்டுமான நடவடிக்கைகள் மற்றும் கழிவுகளை அகற்றுதல்
மற்றும் ஒளி மாசுபாடு செயற்கை விளக்குஎன்ஜி காடழிப்பு மற்றும் வாழ்விட
அழிவுடன் தொடர்புடையது வளர்ச்சியுடன் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீர்கேட்டை மேலும்
அதிகரிக்கிறது பல்லுயிர் இழப்பு.
மாசு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீரழிவின் தாக்கங்கள்
1.மனித ஆரோக்கியம்
மாசுபாடு மனித ஆரோக்கியத்திற்கு குறிப்பிடத்தக்க அபாயங்களை
ஏற்படுத்துகிறது, இதனால் சுவாசம் ஏற்படுகிறது நோய்கள், இருதய பிரச்சினைகள்,
நரம்பியல் கோளாறுகள் மற்றும் பல்வேறு புற்றுநோய்கள். காற்று மாசுபாடு,
குறிப்பாக, முன்கூட்டியே ஏற்படுவதற்கான முக்கிய காரணமாகும் உலகளவில்
இறப்பு, ஆண்டுதோறும் மில்லியன் கணக்கான இறப்புகளுக்கு பங்களிக்கிறது.
நீர்வழி காலரா மற்றும் வயிற்றுப்போக்கு போன்ற நோய்களும் பகுதிகளில் பரவலாக
உள்ளன அசுத்தமான நீர் ஆதாரங்களுடன்.
2.சுற்றுச்சூழல் அமைப்புகள்
மாசுபாடு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீரழிவு ஆகியவை ஆழமான தாக்கங்களை
ஏற்படுத்தும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் அமைப்புகள், உணவு வலைகளை சீர்குலைத்தல்,
வாழ்விடங்களை மாற்றுதல் மற்றும் குறைத்தல் பல்லுயிர். நீர்நிலைகளில் உள்ள
அசுத்தங்கள் நீர்வாழ் உயிரினங்களுக்கு தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும். மீன்,
நீர்வீழ்ச்சிகள் மற்றும் முதுகெலும்பில்லாத உயிரினங்கள் உட்பட, காற்று
மாசுபாடு ஏற்படலாம் தாவரங்கள் மற்றும் மண்ணின் தரத்தை சேதப்படுத்தும்.
வாழ்விட அழிவு மற்றும் துண்டு துண்டானது உயிரினங்களின் உயிர்வாழ்வையும்
சுற்றுச்சூழல் அமைப்பையும் மேலும் அச்சுறுத்துகிறது மீள்தன்மை.
3.காலநிலை மாற்றம்
மாசுபாடு, குறிப்பாக மனித நடவடிக்கைகளிலிருந்து பசுமை இல்ல வாயு
வெளியேற்றம், பூமியில் வெப்பத்தை அடைப்பதன் மூலம் காலநிலை மாற்றத்திற்கு
பங்களிக்கிறது வளிமண்டலம். இது புவி வெப்பமடைதல், கடல் மட்ட உயர்வு, மேலும்
பலவற்றிற்கு வழிவகுக்கிறது அடிக்கடி மற்றும் கடுமையான வானிலை நிகழ்வுகள்,
மாற்றப்பட்ட மழைப்பொழிவு முறைகள் மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் அமைப்புகள் மற்றும்
இனங்கள் விநியோகத்தில் மாற்றங்கள். பருவநிலை மாற்றம் தற்போதுள்ள
சுற்றுச்சூழல் அழுத்தங்களை அதிகப்படுத்துகிறது மற்றும் கூடுதலாக உள்ளது
மனித சமூகங்கள் மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் அமைப்புகளுக்கு
சவால்கள்
4.சமூக பொருளாதார தாக்கங்கள்
மாசுபாடு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீர்கேடு ஆகியவை விகிதாச்சாரத்தில்
பாதிக்கின்றன குறைந்த வருமானம் கொண்ட சமூகங்கள் உட்பட பாதிக்கப்படக்கூடிய
மக்கள், பழங்குடியினர் மக்கள், மற்றும் ஒதுக்கப்பட்ட குழுக்கள். இந்த
சமூகங்கள் பெரும்பாலும் சுமைகளைத் தாங்குகின்றன மாசு தொடர்பான சுகாதார
பிரச்சனைகள், சுற்றுச்சூழல் அநீதிகள் மற்றும் இழப்பு வாழ்வாதாரங்கள்.
சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீர்கேடு பொருளாதாரத்தையும் குறைமதிப்பிற்கு உட்படுத்தும்
வளர்ச்சி, சுற்றுச்சூழல் சேவைகளை குறைத்தல், விவசாய உற்பத்தித்திறன்
மற்றும் சுற்றுலா வருவாய்.
மாசு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீரழிவுக்கான தீர்வுகள்
1.கொள்கை மற்றும் ஒழுங்குமுறை
சட்டங்கள், ஒழுங்குமுறைகள் மற்றும் உட்பட பயனுள்ள சுற்றுச்சூழல் நிர்வாகம்
அமலாக்க வழிமுறைகள், மாசுபாட்டை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதற்கு அவசியம் மற்றும்
சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீரழிவு. உள்ளூர், தேசிய மற்றும் தரநிலைகளை அமைப்பதில்
சர்வதேச நிலைகள் முக்கிய பங்கு வகிக்கின்றன, மாசு அளவைக் கண்காணித்தல்
மற்றும் குறைப்பதற்கான நடவடிக்கைகளை செயல்படுத்துதல் சுற்றுச்சூழல்
பாதிப்புகள். உமிழ்வு வர்த்தக திட்டங்கள் போன்ற கொள்கைகள், மாசு வரிகள்
மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் பாதிப்பு மதிப்பீடுகள் ஊக்கமளிக்கலாம் மாசு குறைப்பு
மற்றும் நிலையான வளர்ச்சி.
2.தொழில்நுட்ப கண்டுபிடிப்பு
தூய்மையான உற்பத்தி செயல்முறைகள் போன்ற தொழில்நுட்பத்தில் முன்னேற்றங்கள்,
புதுப்பிக்கத்தக்க எரிசக்தி தொழில்நுட்பங்கள் மற்றும் மாசுக்கட்டுப்பாட்டு
தொழில்நுட்பங்கள், வழங்குகின்றன மாசுபாட்டைக் குறைப்பதற்கும் சுற்றுச்சூழலை
மேம்படுத்துவதற்கும் வாய்ப்புகள் நிலைத்தன்மை. ஆராய்ச்சி மற்றும்
மேம்பாட்டில் முதலீடுகள் வழிவகுக்கும் மிகவும் திறமையான மற்றும்
சுற்றுச்சூழல் நட்பு தொழில்நுட்பங்களின் வளர்ச்சி எரிசக்தி, போக்குவரத்து,
விவசாயம் உள்ளிட்ட பல்வேறு துறைகளில் மற்றும் கழிவு மேலாண்மை.
3.நிலையான நடைமுறைகள்
நிலையான நடைமுறைகளை ஏற்றுக்கொள்வது மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் நட்பு வாழ்க்கை
முறையை மேம்படுத்துவது மாசுபாடு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீர்கேட்டைக்
குறைக்க உதவும். இதில் அடங்கும் வள நுகர்வு குறைத்தல், கழிவு உற்பத்தியை
குறைத்தல், பாதுகாத்தல் ஆற்றல், மறுசுழற்சி மற்றும் மறுபயன்பாடு ஆகியவற்றை
ஊக்குவித்தல், மற்றும் நிலையானதுக்கு ஆதரவளித்தல் விவசாயம் மற்றும் நில
பயன்பாட்டு நடைமுறைகள். தனிநபர்கள், வணிகங்கள் மற்றும் மேலும் நிலையானதாக
மாறுவதில் சமூகங்கள் அனைத்திற்கும் பங்கு உண்டு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல்
பொறுப்பு நடத்தைகள்.
4.கல்வி மற்றும் விழிப்புணர்வு
பொது விழிப்புணர்வு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் கல்வியை ஊக்குவிப்பது முக்கியம்
மாசுபாடு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் சீரழிவை எதிர்கொள்வதற்கான உத்திகள். கல்வி
பிரச்சாரங்கள் காரணங்கள் மற்றும் பற்றி தனிநபர்களுக்கு தெரிவிக்கலாம்
மாசுபாட்டின் விளைவுகள், நடவடிக்கை எடுக்க அவர்களுக்கு அதிகாரம் அளித்தல்,
மற்றும் ஏ சுற்றுச்சூழல் பொறுப்புணர்வு மற்றும் பொறுப்பு உணர்வு.
சுற்றுச்சூழல் பள்ளிகளில் கல்வித் திட்டங்கள், சமூக நல முயற்சிகள் மற்றும்
ஊடகங்கள் பிரச்சாரங்கள் அனைத்தும் சுற்றுச்சூழலைக் கட்டியெழுப்புவதற்கு
பங்களிக்க முடியும் உணர்வுள்ள சமூகம்.
5.சர்வதேச ஒத்துழைப்பு
மாசுபாடு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் பிரச்சினைகளின் எல்லைக்கு அப்பாற்பட்ட
தன்மையைக் கருத்தில் கொண்டு, இந்த சவால்களை எதிர்கொள்ள சர்வதேச ஒத்துழைப்பு
அவசியம் திறம்பட. பாரீஸ் ஒப்பந்தம் போன்ற பலதரப்பு ஒப்பந்தங்கள் காலநிலை
மாற்றம் மற்றும் ஸ்டாக்ஹோம் மாநாடு தொடர்ந்து கரிம மாசுபடுத்திகள்,
கட்டமைப்புகளை வழங்குகின்றன
Terminologies
1. Air Pollution: Contamination of the atmosphere by harmful substances.
காற்று மாசுபாடு: தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் பொருட்களால் வளிமண்டலம் மாசுபடுதல்.
2. Water Pollution: Contamination of bodies of water by harmful substances.
நீர் மாசுபாடு: தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் பொருட்களால் நீர் நிலைகள் மாசுபடுதல்.
3. Soil Pollution: Contamination of soil by hazardous substances.
மண் மாசுபாடு: அபாயகரமான பொருட்களால் மண் மாசுபடுதல்.
4. Noise Pollution: Excessive or disruptive noise levels.
ஒலி மாசுபாடு: அதிகப்படியான அல்லது சீர்குலைக்கும் ஒலி அளவுகள்.
5. Light Pollution: Excessive or misdirected artificial light.
ஒளி மாசுபாடு: அதிகப்படியான அல்லது தவறாக திசைதிருப்பப்பட்ட செயற்கை ஒளி.
6. Industrial Activities: Processes like manufacturing and power generation releasing pollutants.
தொழில்துறை நடவடிக்கைகள்: உற்பத்தி மற்றும் மின் உற்பத்தி போன்ற செயல்முறைகள் மாசுபடுத்திகளை வெளியிடுகின்றன.
7. Transportation: Emissions from vehicles, airplanes, etc.
, contributing to pollution.
போக்குவரத்து: வாகனங்கள், விமானங்கள் போன்றவற்றிலிருந்து உமிழ்வுகள், மாசுபாட்டிற்கு பங்களிக்கின்றன.
8. Agriculture: Farming practices leading to pollution, like pesticide use.
விவசாயம்: பூச்சிக்கொல்லி பயன்பாடு போன்ற மாசுபாட்டிற்கு வழிவகுக்கும் விவசாய நடைமுறைகள்.
9. Waste Management: Improper disposal of waste causing pollution.
கழிவு மேலாண்மை: மாசுபாட்டை ஏற்படுத்தும் கழிவுகளை முறையற்ற முறையில் அகற்றுதல்.
10. Urbanization and Development: Expansion of cities contributing to various forms of pollution.
நகரமயமாக்கல் மற்றும் வளர்ச்சி: பல்வேறு வகையான மாசுபாட்டிற்கு பங்களிக்கும் நகரங்களின் விரிவாக்கம்.
11. Human Health: Risks to health from pollution, including respiratory issues.
மனித ஆரோக்கியம்: சுவாச பிரச்சினைகள் உட்பட மாசுபாட்டிலிருந்து ஆரோக்கியத்திற்கு ஏற்படும் அபாயங்கள்.
12. Socioeconomic Impacts: Effects on communities and economies.
சமூக பொருளாதார தாக்கங்கள்: சமூகங்கள் மற்றும் பொருளாதாரங்கள் மீதான விளைவுகள்.
13. Policy and Regulation: Government actions to address pollution.
கொள்கை மற்றும் ஒழுங்குமுறை: மாசுபாட்டை நிவர்த்தி செய்வதற்கான அரசாங்கத்தின் நடவடிக்கைகள்.
14. Technological Innovation: Advancements to reduce pollution.
தொழில்நுட்ப கண்டுபிடிப்பு: மாசுபாட்டைக் குறைப்பதற்கான முன்னேற்றங்கள்.
15. Sustainable Practices: Environmentally friendly behaviors.
நிலையான நடைமுறைகள்: சுற்றுச்சூழல் நட்பு நடத்தைகள்.
16. International Cooperation: Global efforts to tackle pollution and environmental issues.
சர்வதேச ஒத்துழைப்பு: மாசுபாடு மற்றும் சுற்றுச்சூழல் பிரச்சினைகளை சமாளிப்பதற்கான உலகளாவிய முயற்சிகள்.
Quick Links
✿ Click Here to Download Preliminary History Study Materials
✿ Click Here to Download History Syllabus for Preliminary
